Delve into the realm of economics with Production Possibilities Curve Practice Worksheet Answers, an authoritative guide that illuminates the intricacies of production possibilities curves (PPCs). This comprehensive resource empowers you with a profound understanding of PPCs, their applications, and the key concepts that underpin them.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the fundamental principles of PPCs, delve into the concept of opportunity cost and trade-offs, and uncover the factors that influence shifts in the PPC. Moreover, we will delve into real-world applications of PPCs, showcasing their significance in economic policy analysis and decision-making.
Production Possibilities Curve Basics

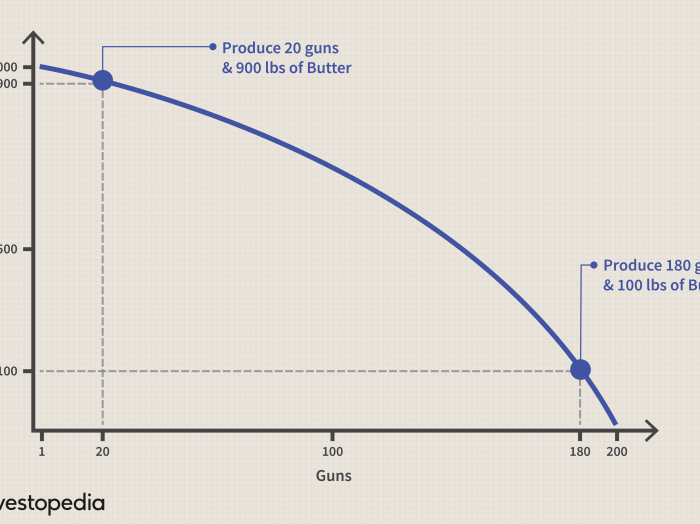
A production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the different combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology. It shows the maximum possible output of one good for any given level of output of the other good, assuming that all resources are fully employed and efficiently utilized.
The PPC is based on the following assumptions:
- The economy has a fixed amount of resources (land, labor, capital, and technology).
- Resources are fully employed and efficiently utilized.
- The production of one good requires the use of some of the resources that could be used to produce the other good.
- Technology is fixed.
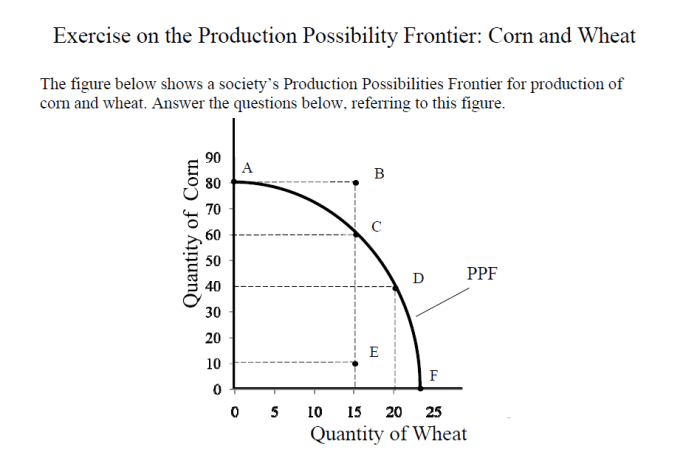
The PPC can be illustrated with a graph, as shown below.

Opportunity Cost and Trade-Offs
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is foregone when a choice is made. In the context of the PPC, opportunity cost is the amount of one good that must be given up in order to produce more of the other good.
The PPC illustrates the opportunity cost of producing more of one good. For example, if an economy decides to produce more cars, it must give up some of the resources that could be used to produce other goods, such as food.
The opportunity cost of producing more cars is the amount of food that must be foregone.
Trade-offs are the choices that must be made when resources are scarce. In the context of the PPC, trade-offs are the decisions about how to allocate resources between the production of different goods.
For example, an economy may decide to produce more cars and fewer computers. This trade-off reflects the decision to allocate more resources to the production of cars and fewer resources to the production of computers.
Shifts in the PPC
The PPC can shift for a variety of reasons, including technological progress, resource availability, and population growth.
- Technological progresscan shift the PPC outward, allowing an economy to produce more of both goods with the same amount of resources.
- Resource availabilitycan shift the PPC outward or inward, depending on whether resources become more or less available.
- Population growthcan shift the PPC outward, as more people are available to work and produce goods.
The following table summarizes the effects of different factors on the PPC.
| Factor | Effect on PPC |
|---|---|
| Technological progress | Outward shift |
| Resource availability | Outward shift or inward shift |
| Population growth | Outward shift |
Applications of the PPC, Production possibilities curve practice worksheet answers
The PPC can be used to analyze economic policies and understand economic growth and development.
For example, the PPC can be used to analyze the effects of a government subsidy on the production of a particular good. The PPC can also be used to understand the effects of a natural disaster on an economy’s ability to produce goods.
The PPC has been used in a variety of real-world decision-making processes. For example, the PPC has been used to help governments make decisions about how to allocate resources between different sectors of the economy.
FAQ Explained: Production Possibilities Curve Practice Worksheet Answers
What is a production possibilities curve (PPC)?
A PPC is a graphical representation of the different combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with its available resources and technology.
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a choice is made.
What are the factors that can cause a PPC to shift?
Factors that can cause a PPC to shift include technological progress, resource availability, and population growth.