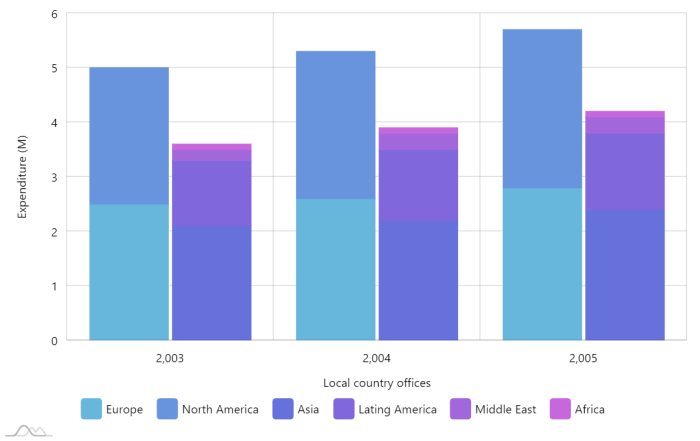
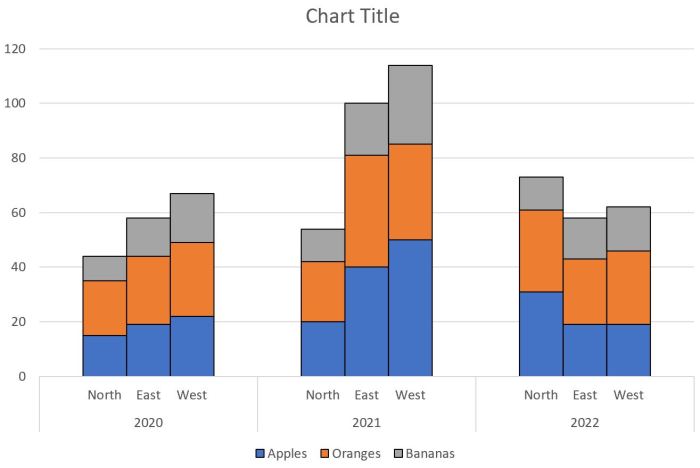
A stacked column chart displays multiple columns for each category – Stacked column charts, a powerful data visualization tool, display multiple columns for each category, enabling the comparison of data series and trends with remarkable clarity. Their versatility and effectiveness make them a cornerstone of data analysis and presentation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of stacked column charts, exploring their advantages, design considerations, and best practices. Through examples and practical insights, we empower you to create impactful visualizations that convey data insights with precision and elegance.
1. Introduction
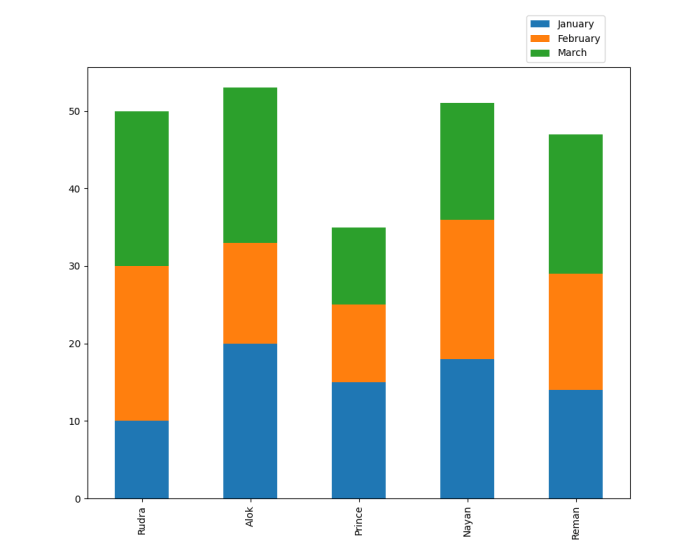
A stacked column chart is a type of bar chart that displays multiple columns for each category. The columns are stacked on top of each other, with the height of each column representing the value of the corresponding data point.
Stacked column charts are often used to compare the values of different categories over time or to show the relative contribution of different factors to a total value.
Answers to Common Questions: A Stacked Column Chart Displays Multiple Columns For Each Category
What is the primary purpose of a stacked column chart?
Stacked column charts are designed to compare the contributions of multiple data series within each category, highlighting the relative proportions and overall trends.
What are the key advantages of using stacked column charts?
Stacked column charts provide a clear visual representation of data, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and outliers. They are also effective for comparing data across multiple categories and subcategories.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when interpreting stacked column charts?
One common pitfall is assuming that the height of each column represents the total value of all data series. It’s important to remember that the height of each segment within a column represents the value of that specific data series.