Charter group ap human geography – Charter groups, central to the study of human geography, play a pivotal role in shaping the human landscape. From their historical evolution to their spatial distribution, the influence of charter groups extends across social, cultural, economic, and political spheres. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of charter groups, providing insights into their profound impact on human societies.
Key Concepts
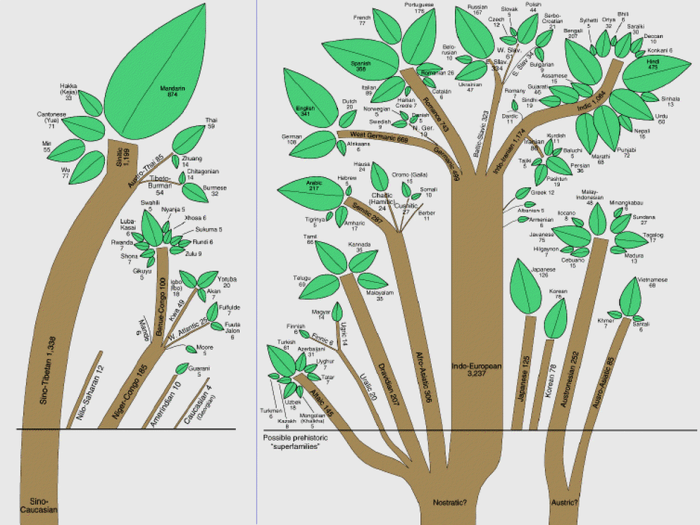
Charter groups are social groups that are defined by a shared identity, culture, or history. They play a significant role in shaping the human landscape by influencing the distribution of people, the development of cities, and the formation of political and economic institutions.
Types of Charter Groups
There are many different types of charter groups, including ethnic groups, religious groups, linguistic groups, and political groups. Each type of charter group has its own unique characteristics and history, and each plays a different role in shaping the human landscape.
- Ethnic groups are groups of people who share a common ancestry and culture. They often have their own language, religion, and customs.
- Religious groups are groups of people who share a common faith. They often have their own set of beliefs, rituals, and practices.
- Linguistic groups are groups of people who share a common language. They often have their own unique way of communicating and expressing themselves.
- Political groups are groups of people who share a common political ideology. They often have their own set of goals and objectives, and they may work together to achieve these goals.
Role of Charter Groups in Shaping the Human Landscape
Charter groups play a significant role in shaping the human landscape by influencing the distribution of people, the development of cities, and the formation of political and economic institutions.
For example, ethnic groups often cluster together in certain areas, creating ethnic enclaves. These enclaves can have a significant impact on the local culture and economy. Religious groups can also cluster together, creating religious communities. These communities can have a significant impact on the local political and social landscape.
Political groups can also play a significant role in shaping the human landscape. For example, political parties can influence the distribution of resources and the development of policies. Economic groups can also play a significant role in shaping the human landscape.
For example, corporations can influence the location of jobs and the development of infrastructure.
Historical Evolution
Charter groups have a long and complex history, dating back to the Middle Ages. In the early days, charter groups were primarily religious organizations, such as monasteries and convents. These groups were often granted special privileges by the government, such as the right to own land and collect taxes.
Over time, charter groups began to take on a more secular role, and they were increasingly used to promote education, healthcare, and other social welfare programs.
Factors Influencing the Development of Charter Groups
A number of factors have influenced the development of charter groups over time. These include:
- The rise of the nation-state:As nation-states became more powerful, they began to assert greater control over the activities of charter groups. This led to a decline in the number of religious charter groups and an increase in the number of secular charter groups.
- The Industrial Revolution:The Industrial Revolution led to a rapid increase in urbanization, which in turn led to a greater demand for social welfare programs. Charter groups were often used to provide these programs, and they played a key role in the development of the modern welfare state.
- The rise of the global economy:In recent decades, the global economy has led to a greater interconnectedness between different parts of the world. This has led to an increase in the number of charter groups that operate across national borders.
Impact of Charter Groups on Major Historical Events
Charter groups have played a significant role in a number of major historical events. For example, charter groups played a key role in the American Revolution, the French Revolution, and the Civil Rights Movement. In each of these cases, charter groups helped to mobilize people and promote social change.
Spatial Distribution
Charter groups are not evenly distributed across the world. Their location and concentration are influenced by various factors, including historical events, cultural traditions, and economic opportunities.
One of the most significant factors determining the spatial distribution of charter groups is their history. Many charter groups originated in specific regions and have remained concentrated in those areas over time. For example, the Basque people are primarily located in the Basque Country, a region that straddles the border between Spain and France.
Natural Resources
The availability of natural resources can also influence the location of charter groups. For example, the Navajo people of the United States are concentrated in the southwestern United States, where they have traditionally relied on sheepherding and farming for their livelihood.
Transportation Networks
Transportation networks can also play a role in the spatial distribution of charter groups. For example, the Chinese diaspora is concentrated in major cities around the world, such as New York City, London, and Sydney. This is because these cities are major transportation hubs that have historically served as gateways for Chinese immigrants.
Political Boundaries
Political boundaries can also affect the spatial distribution of charter groups. For example, the partition of India in 1947 led to the displacement of millions of people, including many charter groups. As a result, there are now significant populations of Indian charter groups in both India and Pakistan.
Social and Cultural Impacts: Charter Group Ap Human Geography
Charter groups exert significant social and cultural influence on the communities they inhabit, shaping local customs, traditions, and beliefs. They play a pivotal role in promoting cultural diversity and fostering social cohesion.
Charter groups often introduce new customs and practices to their communities, enriching the local cultural landscape. They may establish religious institutions, celebrate unique festivals, and share their culinary traditions. This exchange of cultural practices fosters mutual respect and understanding among different groups.
Cultural Diversity
- Charter groups contribute to cultural diversity by introducing new languages, arts, and music to their communities.
- This diversity enriches the local cultural fabric and promotes tolerance and appreciation for different cultures.
Social Cohesion
- Charter groups can strengthen social cohesion by providing a sense of belonging and identity for their members.
- They organize community events, support social welfare initiatives, and foster intergenerational connections.
Economic Implications
- Charter groups can strengthen social cohesion by providing a sense of belonging and identity for their members.
- They organize community events, support social welfare initiatives, and foster intergenerational connections.
Economic Implications
Charter groups can have significant economic implications for local, regional, and national economies. They can create jobs, generate revenue, and promote economic development. However, they can also pose challenges and conflicts with other economic actors.
One of the most important economic benefits of charter groups is their ability to create jobs. Charter groups often employ a large number of people, both directly and indirectly. For example, a charter school may employ teachers, administrators, and support staff.
It may also create jobs for contractors, such as construction workers and janitorial staff. In addition, charter groups can help to create jobs in the surrounding community by attracting new businesses and residents.
Revenue Generation, Charter group ap human geography
Charter groups can also generate significant revenue. This revenue can be used to fund a variety of activities, such as educational programs, community development initiatives, and economic development projects. For example, a charter school may use its revenue to purchase new equipment, hire additional teachers, or provide scholarships to students.
A community development corporation may use its revenue to build affordable housing, create job training programs, or provide other services to the community.
Economic Development
Charter groups can also play a role in promoting economic development. By providing educational opportunities, creating jobs, and generating revenue, charter groups can help to improve the economic well-being of their communities. For example, a charter school may help to improve the educational attainment of its students, which can lead to higher earnings and better job opportunities.
A community development corporation may help to create new businesses and jobs, which can lead to increased economic growth.
However, charter groups can also pose challenges and conflicts with other economic actors. For example, charter schools may compete with traditional public schools for students and resources. Charter groups may also be seen as a threat to businesses that provide similar services, such as private schools or community development organizations.
Political Influence
Charter groups wield significant political influence at local, regional, and national levels. They actively engage in political processes, such as lobbying, voting, and running for office, to advocate for their interests and shape public policy.
Local Governments
At the local level, charter groups influence zoning decisions, educational policies, and community development initiatives. They often form alliances with local officials and participate in public hearings and town hall meetings to express their views and advocate for policies that align with their goals.
Regional Governments
In regional governments, charter groups play a role in shaping policies related to transportation, economic development, and environmental protection. They participate in regional planning commissions and advisory boards, providing input and advocating for policies that support their communities’ interests.
National Governments
At the national level, charter groups engage in lobbying efforts, testifying before congressional committees, and forming coalitions with other organizations to influence policymaking. They work to secure funding for programs that support their members and advocate for policies that align with their values.
Future Trends

The development and evolution of charter groups continue to be shaped by emerging trends that have the potential to transform the future of human geography. These trends include the increasing use of technology, the growing awareness of environmental issues, and the changing nature of work.
The increasing use of technology is having a profound impact on the way that charter groups operate. For example, social media and other online platforms are being used to connect with potential members, organize events, and share information. Additionally, technology is being used to develop new ways to map and analyze spatial data, which is essential for understanding the distribution of charter groups and their impact on the environment.
The growing awareness of environmental issues is also having a significant impact on charter groups. Many charter groups are now focusing on environmental conservation and sustainability. For example, some charter groups are working to protect endangered species, while others are working to reduce pollution and promote renewable energy.
The changing nature of work is also having an impact on charter groups. The traditional 9-to-5 job is becoming increasingly rare, and many people are now working freelance or starting their own businesses. This is creating new opportunities for charter groups to provide services and support to their members.
Potential Implications
These emerging trends have the potential to have a significant impact on the future of human geography. The increasing use of technology could lead to the development of new ways to map and analyze spatial data, which could improve our understanding of the distribution of charter groups and their impact on the environment.
The growing awareness of environmental issues could lead to an increase in the number of charter groups focused on environmental conservation and sustainability. And the changing nature of work could create new opportunities for charter groups to provide services and support to their members.
Role in Shaping the Future of Human Society
Charter groups have the potential to play a significant role in shaping the future of human society. By providing a voice for their members, charter groups can help to influence public policy and decision-making. Additionally, charter groups can provide services and support to their members, which can help to improve their quality of life.
In the future, charter groups are likely to become increasingly important as they play a vital role in addressing the challenges and opportunities facing human society.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key characteristics of charter groups?
Charter groups are typically defined by shared values, goals, and a sense of identity. They may be based on ethnicity, religion, language, or other commonalities.
How do charter groups influence the human landscape?
Charter groups can shape the human landscape through their cultural practices, economic activities, and political participation. They can establish settlements, develop infrastructure, and create distinct cultural identities within a region.
What are the potential challenges faced by charter groups?
Charter groups may face challenges related to discrimination, assimilation, and conflicts with other groups. They may also struggle to maintain their cultural identity while adapting to changing social and economic conditions.